Info
Busycon carica (Gmelin, 1791)
The warty whelk, also known as the prickly fig Busycon carica, is a shell snail in the family Busyconidae, which are colloquially known as Busycon whelks. Members of the family grow quite large and some species are edible.
Busycon carica reaches an impressive size of 30.5cm and is the only species in its genus. Busycon carica are native to the North Atlantic coast of North America from Cape Cod, Massachusetts to northern Florida. This species is common along the Georgia coast.
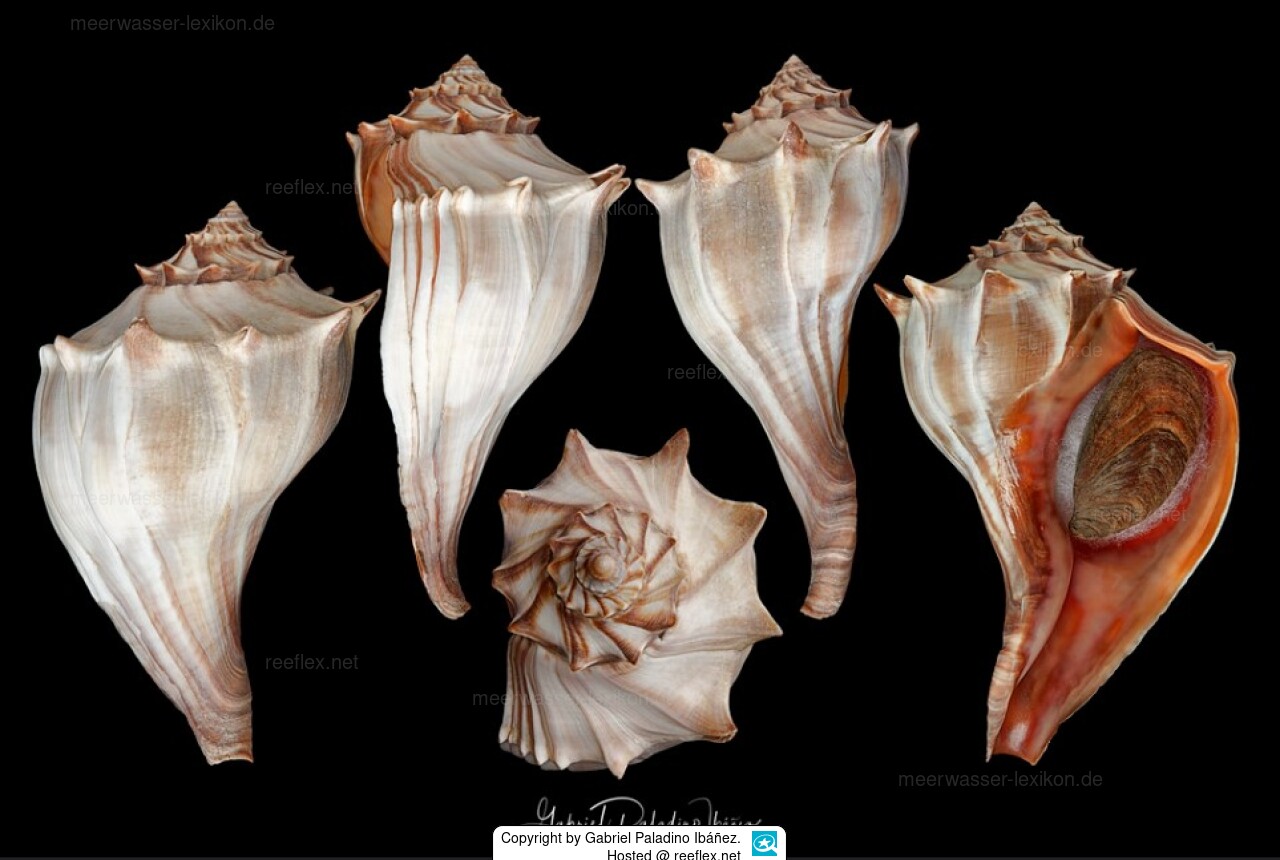
The housing is right-handed and can be closed with an operculum. The shell is thick and strong and has six whorls running in a clockwise direction. The surface has fine stripes and a ring of knob-like projections protrudes at the widest point. The color is ivory or light gray and the large opening (the inside of the opening) is orange.
Busycon carica lives in the intertidal zone and is migratory, switching between deep and shallow water depending on the season. During the weather extremes of the summer and winter months, these sea snails live in deep water up to 150 feet (48 m). During the milder spring and fall weather, they live in shallow water, on coastal or tidal mudflats and sandy areas. In the shallow mudflats, Busycon carica primarily preys on oysters and other sea mussels.
Mating and egg laying occur during spring and fall migration. Internally fertilized eggs are surrounded by a transparent mass of egg white, a gel-like material, and are laid in protective, flat, rounded egg capsules that are connected into a paper-like chain of egg cases called a "mermaid necklace." On average, each capsule contains 0-99 eggs.
After laying their egg cases, females bury one end of the egg cases in the substrate, creating an "anchor" for the developing fertilized eggs and thereby preventing the row of egg cases from washing ashore where they would dry out. Fertilized eggs develop in the capsules. Young hatch with a shell about 2–4 mm long.
Young specimens in particular are eaten by numerous animals, such as crustaceans, horseshoe crabs and fish. Adult snails are eaten by loggerhead sea turtles.
Busycon carica are used by humans as food in dishes such as salads (raw), burgers, donuts and soups. The empty case can be made into a natural bugle by cutting off the top of the spire to form a mouthpiece.
Historically, Native Americans used Busycon carica as a component of wampum, the shell beads that were exchanged for trade in North America.
Synonymised names
Busycon muricatum Röding, 1798 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Fulgur carica (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Murex carica Gmelin, 1791 · unaccepted > superseded combination
Pyrula carica (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Direct children (2)
Subspecies Busycon carica carica (Gmelin, 1791)
Subspecies Busycon carica eliceans (Montfort, 1810)
The warty whelk, also known as the prickly fig Busycon carica, is a shell snail in the family Busyconidae, which are colloquially known as Busycon whelks. Members of the family grow quite large and some species are edible.
Busycon carica reaches an impressive size of 30.5cm and is the only species in its genus. Busycon carica are native to the North Atlantic coast of North America from Cape Cod, Massachusetts to northern Florida. This species is common along the Georgia coast.
The housing is right-handed and can be closed with an operculum. The shell is thick and strong and has six whorls running in a clockwise direction. The surface has fine stripes and a ring of knob-like projections protrudes at the widest point. The color is ivory or light gray and the large opening (the inside of the opening) is orange.
Busycon carica lives in the intertidal zone and is migratory, switching between deep and shallow water depending on the season. During the weather extremes of the summer and winter months, these sea snails live in deep water up to 150 feet (48 m). During the milder spring and fall weather, they live in shallow water, on coastal or tidal mudflats and sandy areas. In the shallow mudflats, Busycon carica primarily preys on oysters and other sea mussels.
Mating and egg laying occur during spring and fall migration. Internally fertilized eggs are surrounded by a transparent mass of egg white, a gel-like material, and are laid in protective, flat, rounded egg capsules that are connected into a paper-like chain of egg cases called a "mermaid necklace." On average, each capsule contains 0-99 eggs.
After laying their egg cases, females bury one end of the egg cases in the substrate, creating an "anchor" for the developing fertilized eggs and thereby preventing the row of egg cases from washing ashore where they would dry out. Fertilized eggs develop in the capsules. Young hatch with a shell about 2–4 mm long.
Young specimens in particular are eaten by numerous animals, such as crustaceans, horseshoe crabs and fish. Adult snails are eaten by loggerhead sea turtles.
Busycon carica are used by humans as food in dishes such as salads (raw), burgers, donuts and soups. The empty case can be made into a natural bugle by cutting off the top of the spire to form a mouthpiece.
Historically, Native Americans used Busycon carica as a component of wampum, the shell beads that were exchanged for trade in North America.
Synonymised names
Busycon muricatum Röding, 1798 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Fulgur carica (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Murex carica Gmelin, 1791 · unaccepted > superseded combination
Pyrula carica (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Direct children (2)
Subspecies Busycon carica carica (Gmelin, 1791)
Subspecies Busycon carica eliceans (Montfort, 1810)






 Gabriel Paladino Ibáñez, Uruguay
Gabriel Paladino Ibáñez, Uruguay

