Info
Paramuricea clavata (Risso, 1826)
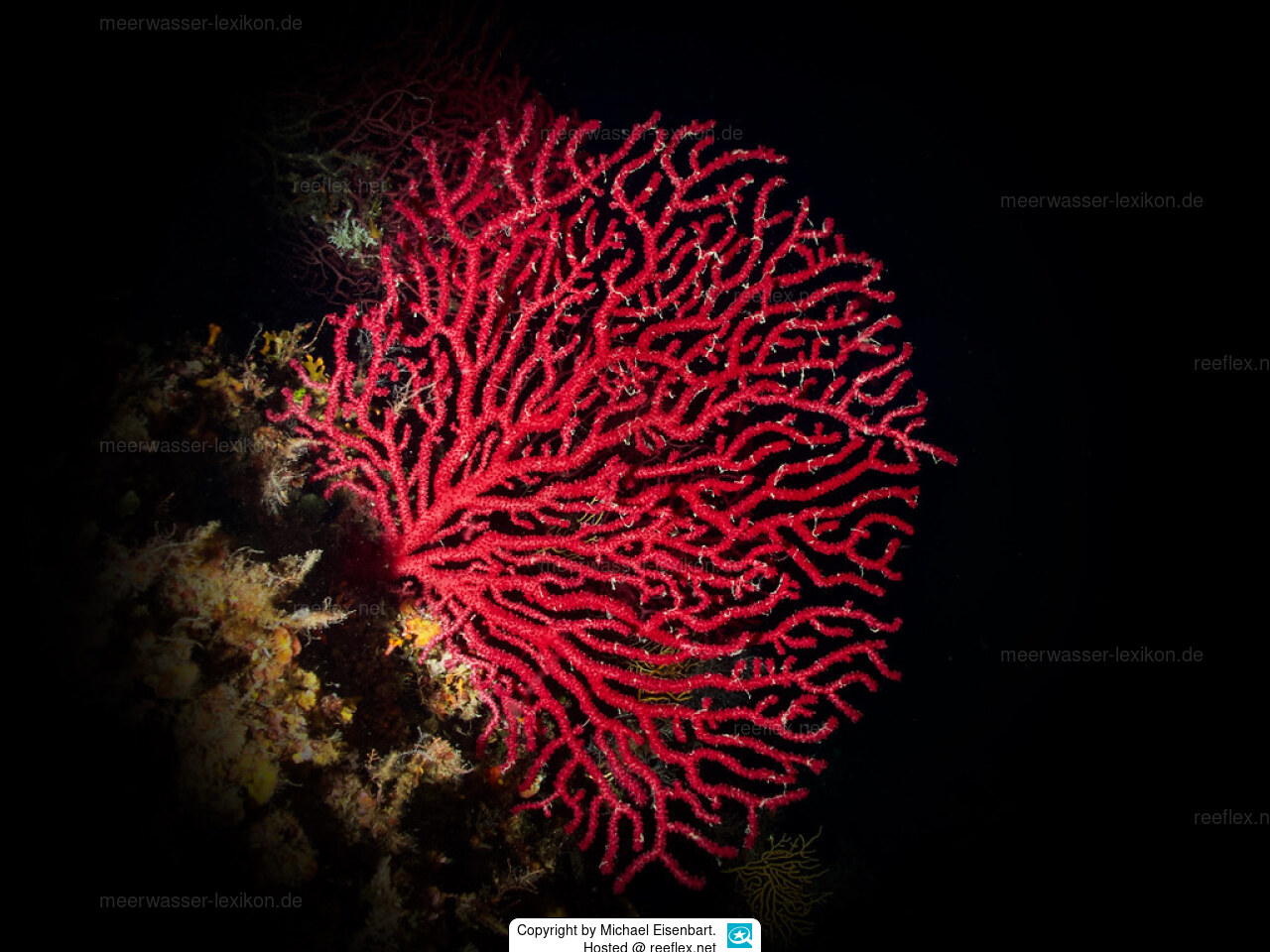
Color: Generally red, in its various tonalities and shades. Pale pink coloration is also found.
Location found (including the present day areas which are no longer exploited):
Italy (Calabria, Campania, Lazio, Toscana, Liguria, Siclia, Sardegna), France, Spain, Morocco, and also Algeria and Tunisia, whose coral, of slightly greater dimensions, was commonly called "barberia"
Recommendation - the coral should be kept in a species-specific tank.
Feeding
Gorgonians do not have zooxanthellae and do not live off light. Azooxanthellate gorgonians do not host symbiotic algae that produce nutrients and energy through photosynthesis.
The pumps should be switched off before feeding. In order for the gorgonian to survive in the aquarium, each individual polyp must be fed sufficiently, i.e. daily or 3-4 times a week. Without feeding, the gorgonian will not survive in the aquarium. The polyps need a certain amount of time to absorb the food (granules or dust food (Ultramarin, Cyclop Eeze) or frozen food (lobster eggs, mysis)). If shrimp and fish are present, they will try to steal the food, so it is essential to feed these cohabitants beforehand.
Newly introduced gorgonian sticks can be stimulated with a liquid food, e.g., PolypLab Polyp, to encourage the individual polyps to open. Only then can feeding be carried out.
The better the individual polyps take up the food provided, the better the growth and reproduction rates will be.
Azooxanthellate corals eat suspensions, marine snow, microplankton, and other organic matter, which is their natural food.
Synonymised names:
Anthomuricea chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Clematissa chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Gorgonia clavata Risso, 1826 (original combination)
Muricea chamaeleon von Koch, 1882 (synonym)
Muriceides chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Paramuricea chamaeleon (von Koch, 1887) (synonym, incorrect authority date)
Paramuricea chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Color: Generally red, in its various tonalities and shades. Pale pink coloration is also found.
Location found (including the present day areas which are no longer exploited):
Italy (Calabria, Campania, Lazio, Toscana, Liguria, Siclia, Sardegna), France, Spain, Morocco, and also Algeria and Tunisia, whose coral, of slightly greater dimensions, was commonly called "barberia"
Recommendation - the coral should be kept in a species-specific tank.
Feeding
Gorgonians do not have zooxanthellae and do not live off light. Azooxanthellate gorgonians do not host symbiotic algae that produce nutrients and energy through photosynthesis.
The pumps should be switched off before feeding. In order for the gorgonian to survive in the aquarium, each individual polyp must be fed sufficiently, i.e. daily or 3-4 times a week. Without feeding, the gorgonian will not survive in the aquarium. The polyps need a certain amount of time to absorb the food (granules or dust food (Ultramarin, Cyclop Eeze) or frozen food (lobster eggs, mysis)). If shrimp and fish are present, they will try to steal the food, so it is essential to feed these cohabitants beforehand.
Newly introduced gorgonian sticks can be stimulated with a liquid food, e.g., PolypLab Polyp, to encourage the individual polyps to open. Only then can feeding be carried out.
The better the individual polyps take up the food provided, the better the growth and reproduction rates will be.
Azooxanthellate corals eat suspensions, marine snow, microplankton, and other organic matter, which is their natural food.
Synonymised names:
Anthomuricea chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Clematissa chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Gorgonia clavata Risso, 1826 (original combination)
Muricea chamaeleon von Koch, 1882 (synonym)
Muriceides chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)
Paramuricea chamaeleon (von Koch, 1887) (synonym, incorrect authority date)
Paramuricea chamaeleon (von Koch, 1882) (synonym)






 Michael Eisenbart
Michael Eisenbart















